Back pain, a common complaint that affects millions worldwide, can be a debilitating condition impacting one's daily life. Whether it's a dull ache or a sharp, shooting sensation, back pain can significantly hinder mobility and overall well-being. The condition can affect any part of the back, from the neck to the lower back. However, with the proper knowledge and approach, you can find effective ways to alleviate discomfort and regain control over your life. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, and back pain diagnosis while offering practical prevention strategies, treatment options, and rehabilitation techniques.
Back pain symptoms can vary and depend on the underlying cause and severity. Some common symptoms include:
Back pain can stem from various causes, ranging from lifestyle factors to underlying medical conditions. Some of the most common causes include:
To effectively treat back pain, it's crucial to identify the underlying cause. Your doctor may recommend one or more of the following diagnostic tests:
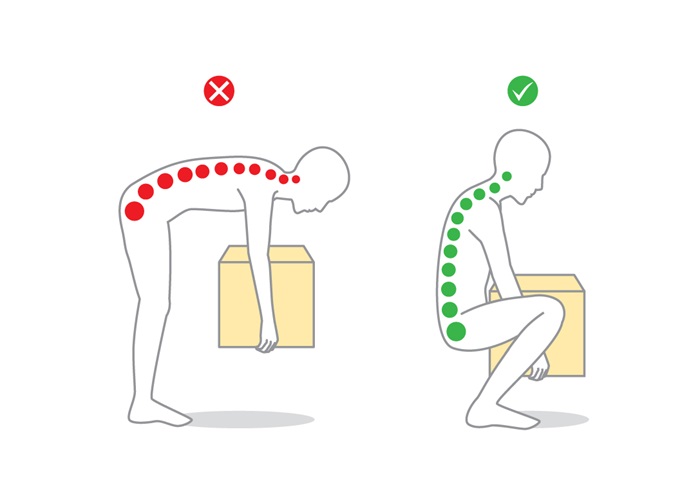
While back pain can be challenging to avoid entirely, there are numerous preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk:
Depending on the severity and cause of your upper, lower or middle back pain, various treatment options are available:

After receiving treatment for back pain, following a comprehensive rehabilitation plan to promote healing and prevent future recurrences is crucial. This plan may involve:
Several home remedies for lower back pain and self-care practices can provide back pain relief for mild to moderate back pain:
In addition to conventional management, some individuals may find relief through alternative therapies:
For those dealing with chronic back pain, managing the condition can be a lifelong journey. Here are some strategies to improve your quality of life:
Regarding back pain, several myths and misconceptions can hinder effective treatment and recovery. Here are some common misconceptions debunked:
Myth: Bed rest is the best remedy for back pain.
Fact: While rest may be necessary for severe cases, prolonged bed rest can weaken the back muscles and delay recovery. Doctors generally recommend gentle stretching and exercise.
Myth: Back pain is a normal part of ageing
Fact: While the risk of back pain may increase with age due to degenerative conditions, it is not an inevitable consequence of getting older. Proper care and preventive measures can help minimise back pain.
Myth: Back surgery is the only solution for severe back pain.
Fact: Surgery is usually considered a last resort when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. Many instances of back pain can be managed through non-surgical methods.
Myth: Lifting heavy items is the primary cause of lower back pain.
Fact: While improper lifting techniques can contribute to back pain, other factors like poor posture, sedentary lifestyle, and underlying conditions can also play a role.
Myth: Back pain always indicates a serious underlying condition.
Fact: While muscle strain, poor posture, or minor injuries often cause back pain, you can effectively manage it with conservative measures. However, back pain can sometimes signal a more serious condition.
When to see a Doctor
Persistent or severe back pain often warrants a visit to an orthopaedic doctor. Seek medical attention if:
What is the cause of back pain?
Various causes can contribute to back pain, including muscle strain, herniated discs, arthritis, spinal stenosis, skeletal irregularities, and obesity. Identifying the cause of the underlying back pain is crucial for effective back pain treatment.
How to reduce back pain?
You can try over-the-counter pain medications to reduce back pain, apply heat or cold therapy, practice gentle stretching and exercise, maintain proper posture, and manage stress. If the pain persists, seek medical attention for appropriate treatment.
How did I cure my back pain?
Curing back pain involves a combination of treatments, such as physical therapy for lower back pain, chiropractic care, massage therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. The specific treatment approach is based on the underlying cause and severity of the pain.
How do I know if my back pain is serious?
Signs that your back pain may be serious include severe or worsening pain, numbness or weakness in the legs, loss of bowel or bladder control, and fever or unexplained weight loss. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical guidance immediately.
Is bad back pain normal?
While mild back pain is common and often related to muscle strain or poor posture, severe or persistent back pain is not normal and should be evaluated by a doctor.
How do you tell if back pain is muscular or kidney?
Muscular back pain generally feels like a dull ache or tightness. On the other hand, kidney-related pain is typically felt as lower back pain just above the hips and may be accompanied by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or fever. If you suspect kidney-related issues, seek medical attention promptly.