Haemorrhoids, or piles, are swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus caused by increased pressure during bowel movements, pregnancy, or prolonged sitting. They are classified as internal or external, with symptoms such as bleeding, itching, and discomfort. Treatment options range from home remedies to medical interventions like surgery. Seek medical advice if symptoms persist.
Haemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are swollen or inflamed blood vessels located in the rectum or anus. These occur when veins in this region experience excessive pressure, leading to discomfort and other symptoms. Haemorrhoids can affect anyone but are particularly common in individuals with chronic constipation, obesity, or pregnancy.
While haemorrhoids are not typically life-threatening, they can significantly impact daily life, causing discomfort during sitting, walking, or bowel movements.
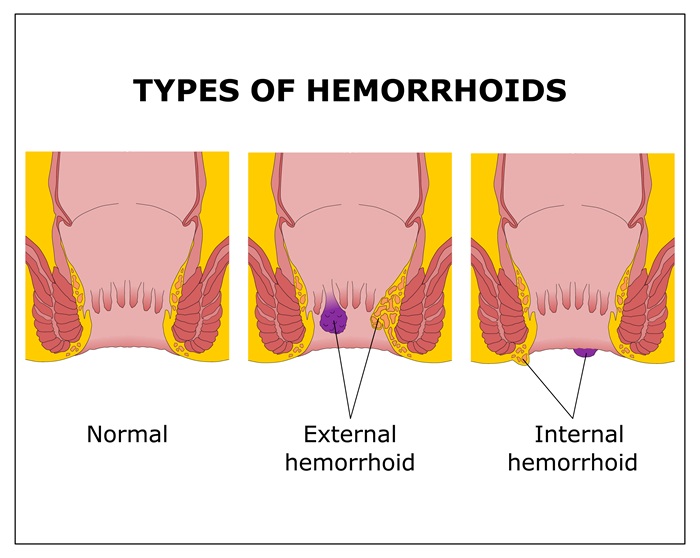
Haemorrhoids are classified into two main categories:
Internal haemorrhoids are found inside the rectum and typically don’t cause pain, as this area lacks pain-sensitive nerves. However, they may lead to noticeable symptoms like bright red blood during bowel movements or a feeling of tissue protruding from the anus during straining.
External haemorrhoids develop beneath the skin surrounding the anus, an area rich in pain-sensitive nerves. They can lead to discomfort, swelling, and itching, with severe pain occurring if a blood clot forms within the swollen tissue.
The haemorrhoids symptoms you experience depend on whether they are internal or external:
Symptoms of piles in females may worsen during pregnancy due to increased pressure on pelvic veins. Symptoms of piles in males are often linked to heavy lifting or chronic constipation.
Haemorrhoids causes are linked to increased pressure in the rectal or anal veins. Factors include:
Diagnosing haemorrhoids involves a combination of medical history and physical examination. A doctor may:
In some cases, additional tests may be needed to rule out other conditions, like colorectal cancer, especially if bleeding is a primary symptom.
Haemorrhoids treatment varies depending on severity. Options include:
For a piles problem, doctors may prescribe piles medicine like creams or oral pain relievers to manage symptoms.
If home remedies and piles medicine don’t provide relief or symptoms worsen, it’s time to consult a specialist. Persistent bleeding, extreme pain, or recurrent prolapse requires medical intervention.
For residents of Bangalore, you can visit the nearest SPARSH Hospital. We are renowned for reputable gastroenterology hospitals in Bangalore. At our hospitals you can consult with experienced gastroenterologists in Bangalore, who can offer effective diagnosis and treatment.
Haemorrhoids can be uncomfortable but are manageable with timely care and lifestyle changes. Recognizing symptoms early, maintaining a fibre-rich diet, and avoiding prolonged sitting are key preventive measures. If symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice.
What is the difference between haemorrhoids and piles?
Haemorrhoids and piles are just different names for the same condition—swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus.
What are the main causes of haemorrhoids?
The main causes include straining during bowel movements, sitting for long periods, pregnancy, obesity, and a low-fibre diet.
Do haemorrhoids (piles) go away?
Mild haemorrhoids can improve with lifestyle changes, but more severe cases may need medical treatment.
What is the fastest way to heal a haemorrhoid?
A combination of warm sitz baths, topical creams, and a high-fibre diet can help heal haemorrhoids faster.
Are haemorrhoids (piles) harmful?
While they aren’t life-threatening, untreated haemorrhoids can lead to significant discomfort, bleeding, and complications like anaemia.
Categories: Gastroenterology
Hemorrhoids (Piles): Symptoms, causes, and treatments is available for appointments. Please fill the below form to book an appointment.
Unlock the door to exceptional healthcare, book an appointment with SPARSH Hospital and let your journey to wellness begin.